Principles Of Translation Book Pdf Free Download
 At that place are a bewildering number of different types of translation.
At that place are a bewildering number of different types of translation.
So we've identified the 51 types you're most likely to come up across, and explain exactly what each one means.
This includes all the main translation methods, techniques, strategies, procedures and areas of specialisation.
It'southward our way of helping you brand sense of the many dissimilar kinds of translation – and deciding which ones are correct for you.
Don't miss our free summary pdf download later in the article!
The 51 types of translation nosotros've identified fall neatly into four singled-out categories.
Translation Category A: 15 types of translation based on the technical field or subject area of the text
 Translation companies oft define the various kinds of translation they provide co-ordinate to the field of study area of the text.
Translation companies oft define the various kinds of translation they provide co-ordinate to the field of study area of the text.
This is a useful way of classifying translation types considering specialist texts normally require translators with specialist knowledge.
Hither are the most common types you lot're like to come beyond in this category.
1. Full general Translation
What is information technology?
The translation of non-specialised text. That is, text that nosotros can all understand without needing specialist noesis in some area.
The text may still contain some technical terms and jargon, but these will either exist widely understood, or hands researched.
What this ways
The implication is that you don't need someone with specialist cognition for this type of translation – any professional translator tin handle them.
Translators who only practise this kind of translation (don't have a specialist field) are sometimes referred to every bit 'generalist' or 'full general purpose' translators.
Examples
Nigh concern correspondence, website content, company and product/service info, not-technical reports.
Most of the residuum of the translation types in this Category practice require specialist translators.
Bank check out our video on 13 types of translation requiring special translator expertise:
2. Technical Translation
What is it?
We apply the term "technical translation" in two different ways:
Broad meaning: any translation where the translator needs specialist knowledge in some domain or area.
This definition would include almost all the translation types described in this section.
Narrow meaning: limited to the translation of technology (in all its forms), IT and industrial texts.![]()
This narrower pregnant would exclude legal, financial and medical translations for example, where these would be included in the broader definition.
What this means
Technical translations require knowledge of the specialist field or domain of the text.
That's because without it translators won't completely understand the text and its implications. And this is essential if we want a fully accurate and appropriate translation.
Good to know
Many technical translation projects as well have a typesetting/dtp requirement. Be certain your translation provider can handle this component, and that you lot've allowed for it in your projection costings and fourth dimension frames.
Examples
Manuals, specialist reports, production brochures
3. Scientific Translation
What is information technology?
The translation of scientific research or documents relating to information technology.![]()
What this means
These texts invariably contain domain-specific terminology, and often involve cutting border enquiry.
And so it's imperative the translator has the necessary knowledge of the field to fully empathize the text. That'southward why scientific translators are typically either experts in the field who take turned to translation, or professionally qualified translators who also have qualifications and/or experience in that domain.
On occasion the translator may take to consult either with the author or other domain experts to fully comprehend the material and and then translate information technology accordingly.
Examples
Inquiry papers, journal articles, experiment/trial results.
iv. Medical Translation
What is it?
The translation of healthcare, medical production, pharmaceutical and biotechnology materials.
Medical translation is a very broad term roofing a wide diverseness of specialist areas and materials – everything from patient information to regulatory, marketing and technical documents.
Every bit a issue, this translation blazon has numerous potential sub-categories – 'medical device translations' and 'clinical trial translations', for example.![]()
What this ways
As with whatever text, the translators need to fully understand the materials they're translating. That means sound knowledge of medical terminology and they'll often too demand specific bailiwick-thing expertise.
Expert to know
Many countries accept specific requirements governing the translation of medical device and pharmaceutical documentation. This includes both your client-facing and product-related materials.
Examples
Medical reports, product instructions, labeling, clinical trial documentation
5. Financial Translation
What is it?
In broad terms, the translation of banking, stock exchange, forex, financing and fiscal reporting documents.
However, the term is generally used only for the more technical of these documents that require translators with cognition of the field.
Any competent translator could translate a depository financial institution argument, for example, so that wouldn't typically be considered a financial translation.![]()
What this means
Yous need translators with domain expertise to correctly understand and translate the fiscal terminology in these texts.
Examples
Company accounts, annual reports, fund or product prospectuses, audit reports, IPO documentation
six. Economic Translations
What is it?
1. Sometimes used as a synonym for financial translations.
two. Other times used somewhat loosely to refer to any area of economic activity – so combining business concern/commercial, financial and some types of technical translations.
3. More narrowly, the translation of documents relating specifically to the economy and the field of economics.![]()
What this means
Every bit ever, you need translators with the relevant expertise and noesis for this type of translation.
7. Legal Translation
What is it?
The translation of documents relating to the constabulary and legal process.![]()
What this means
Legal texts require translators with a legal background.
That'south because without it, a translator may not:
– fully understand the legal concepts
– write in legal way
– sympathize the differences between legal systems, and how all-time to interpret concepts that don't correspond.
And we need all that to produce professional quality legal translations – translations that are authentic, terminologically correct and stylistically appropriate.
Examples
Contracts, legal reports, courtroom judgments, expert opinions, legislation
8. Juridical Translation
What is it?
one. More often than not used equally a synonym for legal translations.
two. Alternatively, can refer to translations requiring some course of legal verification, certification or notarization that is common in many jurisdictions.![]()
9. Judicial Translation
What is it?
1. Most commonly a synonym for legal translations.
two. Rarely, used to refer specifically to the translation of courtroom proceeding documentation – then judgments, minutes, testimonies, etc.
x. Patent Translation
What is information technology?
The translation of intellectual holding and patent-related documents.![]()
Central features
Patents have a specific construction, established terminology and a requirement for complete consistency throughout – read more on this here. These are central aspects to patent translations that translators need to get right.
In addition, subject affair tin exist highly technical.
What this means
You need translators who have been trained in the specific requirements for translating patent documents. And with the domain expertise needed to handle whatever technical content.
Examples
Patent specifications, prior fine art documents, oppositions, opinions
11. Literary Translation
What is information technology?
The translation of literary works – novels, short stories, plays, essays, poems.
![]()
Key features
Literary translation is widely regarded every bit the most difficult form of translation.
That'south because it involves much more than simply carrying all meaning in an advisable mode. The translator's challenge is to as well reproduce the character, subtlety and impact of the original – the essence of what makes that work unique.
This is a monumental job, and why it'south oft said that the translation of a literary work should be a literary piece of work in its own right.
What this means
Literary translators must be talented wordsmiths with exceptional creative writing skills.
Because few translators take this skillset, you lot should but consider dedicated literary translators for this type of translation.
12. Commercial Translation
What is it?
The translation of documents relating to the globe of business.
This is a very generic, wide-reaching translation type. It includes other more specialised forms of translation – legal, financial and technical, for instance. And all types of more general business documentation.
Likewise, some documents will crave familiarity with concern jargon and an ability to write in that style.![]()
What this means
Unlike translators volition be required for different certificate types – specialists should handle materials involving technical and specialist fields, whereas generalist translators can translate not-specialist materials.
Examples
Business organisation correspondence, reports, marketing and promotional materials, sales proposals
13. Business Translations
What is it?
A synonym for Commercial Translations.
xiv. Authoritative Translations
What is it?
The translation of business organization management and administration documents.
Then it's a subset of business organization / commercial translations.![]()
What this means
The implication is these documents volition include business jargon and 'management speak', then require a translator familiar with, and practised at, writing in that fashion.
Examples
Management reports and proposals
15. Marketing Translations
What is it?
The translation of advertising, marketing and promotional materials.
This is a subset of business or commercial translations.
Key features
Marketing re-create is designed to accept a specific impact on the audience – to appeal and persuade.
And then the translated copy must exercise this too.
But a direct translation volition seldom accomplish this – so translators demand to adapt their wording to produce the impact the text is seeking.
And sometimes a completely new message might be needed – encounter transcreation in our next category of translation types.
What this means
Marketing translations require translators who are skilled writers with a flair for producing persuasive, impactful copy.
Equally relatively few translators have these skills, engaging the right translator is key.
Practiced to know
This type of translation often comes with a typesetting or dtp requirement – particularly for adverts, posters, brochures, etc.
Its best for your translation provider to handle this component. That'due south because multilingual typesetters sympathize the design and aesthetic conventions in other languages/cultures. And these are essential to ensure your materials have the desired impact and appeal in your target markets.
Examples
Advertisement, brochures, some website/social media text.
Translation Category B: 14 types of translation based on the terminate product or utilize of the translation
This category is all virtually how the translation is going to be used or the terminate product that'south produced.
Well-nigh of these types involve either adapting or processing a completed translation in some mode, or converting or incorporating information technology into some other program or format.
You'll see that some are very specialised, and complex.
It's another way translation providers refer to the range of services they provide.
Bank check out our video of the most specialised of these types of translation:
16. Document Translations
What is it?
The translation of documents of all sorts.
Hither the translation itself is the end product and needs no further processing beyond standard formatting and layout.
17. Text Translations
What is it?
A synonym for document translation.
xviii. Certified Translations
What is it?
A translation with some grade of certification.
Key features
The certification tin can take many forms. It can exist a statement past the translation visitor, signed and dated, and optionally with their company seal. Or a similar certification by the translator.
The verbal format and wording volition depend on what clients and authorities require – here's an example.
nineteen. Official Translations
What is information technology?
1. Mostly used equally a synonym for certified translations.
2. Can also refer to the translation of 'official' documents issued by the authorities in a strange state. These will near always need to be certified.
20. Software Localisation
What is it?
Adapting software for another language/civilization.
Key features
The goal of software localisation is non just to make the program or production available in other languages. It's also well-nigh ensuring the user experience in those languages is as natural and effective as possible.
Translating the user interface, messaging, documentation, etc is a major role of the process.
Likewise cardinal is a customisation process to ensure everything matches the conventions, norms and expectations of the target cultures.
Adjusting time, date and currency formats are examples of simple customisations. Others might involve adapting symbols, graphics, colours and fifty-fifty concepts and ideas.
Localisation is often preceded past internationalisation – a review process to ensure the software is optimally designed to handle other languages.
And information technology's nigh always followed by thorough testing – to ensure all text is in the correct identify and fits the space, and that everything makes sense, functions equally intended and is culturally appropriate.
Localisation is often abbreviated to L10N, internationalisation to i18n.
What this ways
Software localisation is a specialised kind of translation, and you should always appoint a company that specialises in it.
They'll have the systems, tools, personnel and experience needed to achieve top quality outcomes for your product.
21. Game Localisation
What is it?
Adapting games for other languages and markets.
Information technology's a subset of software localisation.
Key features
The goal of game localisation is to provide an engaging and fun gaming feel for speakers of other languages.
It involves translating all text and recording any required foreign language audio.
But too adapting annihilation that would clash with the target culture's community, sensibilities and regulations.
For case, content involving alcohol, violence or gambling may either be censored or inappropriate in the target market.
And at a more bones level, anything that makes users experience uncomfortable or awkward will detract from their feel and thus the success of the game in that market.
And so portions of the game may have to be removed, added to or re-worked.
Game localisation involves at least the steps of translation, adaptation, integrating the translations and adaptations into the game, and testing.
What this means
Game localisation is a very specialised blazon of translation best left to those with specific expertise and experience in this area.
22. Multimedia Localisation
What is it?
Adapting multimedia for other languages and cultures.
Multimedia refers to any textile that combines visual, audio and/or interactive elements. So videos and movies, on-line presentations, due east-Learning courses, etc.![]()
Central features
Anything a user can run into or hear may need localising.
That ways the audio and any text appearing on screen or in images and animations.
Plus it can mean reviewing and adapting the visuals and/or script if these aren't suitable for the target culture.
The localisation process volition typical involve:
– Translation
– Modifying the translation for cultural reasons and/or to meet technical requirements
– Producing the other language versions
Audio output may be vocalisation-overs, dubbing or subtitling.
And output for visuals can involve re-creating elements, or supplying the translated text for the designers/engineers to contain.
What this means
Multimedia localisation projects vary hugely, and it's essential your translation providers have the specific expertise needed for your materials.
23. Script Translations
What is information technology?
Preparing the text of recorded material for recording in other languages.
Fundamental features
In that location are several issues with script translation.
One is that translations typically cease up longer than the original script. So voicing the translation would take upward more than space/fourth dimension on the video than the original language.
Sometimes that infinite will be bachelor and this will be OK.
But mostly it won't be. So the translation has to be edited back until it can be comfortably voiced inside the time available on the video.
Another challenge is the translation may accept to synchronise with specific actions, animations or text on screen.
Besides, some scripts also bargain with technical subject areas involving specialist technical terminology.
Finally, some scripts may be very culture-specific – featuring humour, community or activities that won't work well in another linguistic communication. Here the script, and sometimes also the associated visuals, may demand to exist adjusted before beginning the translation procedure.
It goes without proverb that a script translation must exist done well. If it's not, in that location'll exist problems producing a expert foreign language sound, which will compromise the effectiveness of the video.
Translators typically work from a time-coded transcript. This is the original script marked to show the time available for each section of the translation.
What this ways
In that location are several potential pitfalls in script translations. So information technology's vital your translation provider is proficient at this blazon of translation and able to handle whatsoever technical content.
24. Vox-over and Dubbing Projects
What is it?
Translation and recording of scripts in other languages.
Vox-overs vs dubbing
In that location is a technical difference.
A voice-over adds a new track to the production, dubbing replaces an existing one.
Key features
These projects involve two parts:
– a script translation (as described above), and
– producing the audio
So they involve the combined efforts of translators and voice artists.![]()
The task for the vocalism artist is to produce a high quality read. That's one that matches the style, tone and richness of the original.
Often each section of the new sound will need to be the same length every bit the original.
But sometimes the segments will demand to be shorter – for example where the voice-over lags the original by a 2nd or two. This is mutual in interviews etc, where the original voice is heard initially then drops out.
The nigh difficult form of dubbing is lip-syncing – where the new audio needs to synchronise with the original speaker's lip movements, gestures and deportment.
Lip-syncing requires an exceptionally skilled vocalism talent and considerable time spent rehearsing and fine tuning the translation.
What this means
You need to use experienced professionals every step of the way in this type of projection.
That's to ensure firstly that your foreign-linguistic communication scripts are get-go class, then that the voicing is of loftier professional person standard.
Anything less volition mean your foreign language versions will exist way less effective and appealing to your target audience.
25. Subtitle Translations
What is it?
Producing strange language captions for sub or surtitles.
Key features
The goal with subtitling is to produce captions that viewers tin comfortably read in the time available and still follow what'due south happening on the video.
To achieve this, languages have "rules" governing the number of characters per line and the minimum time each subtitle should brandish.
Sticking to these guidelines is essential if your subtitles are to be effective.
But this is no easy task – it requires simple linguistic communication, short words, and a very succinct style. Translators volition spend considerable time mulling over and re-working their translation to become it only right.
Most subtitle translators utilize specialised software that will output the captions in the format sound engineers need for incorporation into the video.
What this means
Every bit with other specialised types of translation, yous should merely utilize translators with specific expertise and experience in subtitling.
26. Website Localisation
What is it?
The translation and adapting of relevant content on a website to best suit the target language and civilization.
Notation: Many providers utilize the term website translation as a synonym for localisation. Strictly speaking though, translation is just one office of localisation.
Key features
- Not all pages on a website may need to be localised – clients should review their content to place what's relevant for the other language versions.
- Some content may need specialist translators – legal and technical pages for example.
- There may besides be videos, linked documents, and text or captions in graphics to translate.
- Accommodation tin can hateful irresolute appointment, time, currency and number formats, units of measure out, etc.
- Just also images, colours and even the overall site design and style if these won't have the desired touch on in the target culture.
- Translated files tin be supplied in a broad range of formats – translators usually coordinate output with the site webmasters.
- New language versions are usually thoroughly reviewed and tested before going alive to confirm everything is displaying correctly, works as intended and is cultural advisable.
What this means
The first step should be to review your content and identify what needs to exist translated. This might lead you to alter some pages for the foreign language versions.
In choosing your translation providers be sure they tin can:
– handle any technical or legal content,
– provide your webmaster with the file types they desire.
And yous should e'er get your translators to systematically review the foreign language versions before going live.
27. Transcreation
What is it?
Adapting a message to arm-twist the aforementioned emotional response in some other language and culture.
Translation is all well-nigh carrying the message or pregnant of a text in another language. Just sometimes that message or meaning won't have the desired effect in the target civilisation.
This is where transcreation comes in. Transcreation creates a new message that will go the desired emotional response in that culture, while preserving the style and tone of the original.
And then it'southward a sort of artistic translation – which is where the word comes from, a combination of 'translation' and 'cosmos'.
At i level transcreation may be as elementary as choosing an advisable idiom to convey the same intent in the target language – something translators do all the time.
Simply mostly the term is used to refer to adapting primal advert and marketing messaging. Which requires copywriting skills, cultural awareness and an excellent noesis of the target marketplace.
Who does it?
Some translation companies have suitably skilled personnel and offer transcreation services.
Ofttimes though information technology's washed in the target country by specialist copywriters or an advertising or marketing agency – particularly for significant campaigns and to institute a brand in the target marketplace.
What this means
Most general marketing and promotional texts won't need transcreation – they can be handled past a translator with fantabulous creative writing skills.
But slogans, by-lines, advertising copy and branding statements frequently practise.
Whether you should opt for a translation company or an in-market agency volition depend on the nature and importance of the material, and of course your budget.
28. Audio Translations
What is it?
Broad meaning: the translation of whatever type of recorded material into another language.
More than normally: the translation of a foreign linguistic communication video or audio recording into your own language. And then this is where y'all want to know and certificate what a recording says.
Fundamental features
The beginning challenge with sound translations is it'south often incommunicable to selection upward every give-and-take that's said. That's considering audio quality, speech clarity and speaking speed can all vary enormously.
It'southward also a mentally challenging job to listen to an audio and translate information technology directly into another language. Information technology's easy to miss a word or an aspect of meaning.
So best practice is to kickoff transcribe the sound (type up exactly what is said in the language it is spoken in), then translate that transcription.
Still, this is time consuming and therefore costly, and there are other options if lesser precision is adequate.
What this means
It'southward best to discuss your requirements for this kind of translation with your translation provider. They'll be able to propose the best translation process for your needs.
Examples
Interviews, product videos, police recordings, social media videos.
29. Translations with DTP
What is it?
Translation incorporated into graphic design files.
Central features
Graphic blueprint programs are used by professional person designers and graphic artists to combine text and images to create brochures, books, posters, packaging, etc.
Translation plus dtp projects involve 3 steps – translation, typesetting, output.
The typesetting component requires specific expertise and resources – software and fonts, typesetting know-how, an appreciation of foreign language display conventions and aesthetics.
What this ways
Make sure your translation company has the required multilingual typesetting/desktop publishing expertise whenever yous're translating a document created in a graphic design program.
Translation Category C: xiii types of translation based on the translation method employed
This category has two sub-groups:
– the applied methods translation providers employ to produce their translations, and
– the translation strategies/methods identified and discussed within academia.
The translation methods translation providers employ
In that location are 4 main methods used in the translation industry today. We have an overview of each below, only for more particular, including when to utilize each one, see our comprehensive blog article.
Or lookout our video.
Important: If you're a customer you need to empathize these 4 methods – cull the incorrect 1 and the translation you terminate up with may not come across your needs!
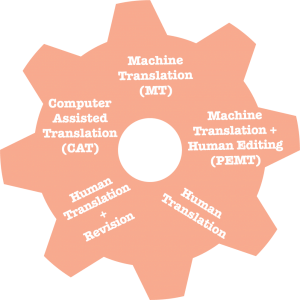
thirty. Car Translation (MT)
What is it?
A translation produced entirely by a software program with no human intervention.
A widely used, and free, example is Google Translate. And in that location are also commercial MT engines, generally tailored to specific domains, languages and/or clients.
Pros and cons
There are 2 limitations to MT:
– they make mistakes (incorrect translations), and
– quality of diction is patchy (some parts good, others unnatural or fifty-fifty nonsensical)
On they positive side they are virtually instantaneous and many are complimentary.
All-time suited for:
Getting the full general idea of what a text says.
This method should never be relied on when loftier accurateness and/or good quality wording is needed.
31. Machine Translation plus Human Editing (PEMT)
What is it?
A automobile translation subsequently edited past a human translator or editor (often called Mail service-editing Automobile Translation = PEMT).
The editing process is designed to rectify some of the deficiencies of a car translation.
This process can take different forms, with different desired outcomes. Probably well-nigh mutual is a 'lite editing' procedure where the editor ensures the text is understandable, without trying to gear up quality of expression.
Pros and cons
This method won't necessarily eliminate all translation mistakes. That's because the plan may have chosen a wrong word (meaning) that wasn't obvious to the editor.
And wording won't generally be as expert as a professional human translator would produce.
Its advantage is information technology's generally quicker and a little cheaper than a full translation by a professional translator.
All-time suited for:
Translations for information purposes merely.
Again, this method shouldn't be used when total accuracy and/or consistent, natural wording is needed.
32. Human Translation
What is it?
Translation by a professional human translator.
Pros and cons
Professional translators should produce translations that are fully accurate and well-worded.
That said, there is always the possibility of 'human error', which is why translation companies like usa typically offering an boosted review process – run across side by side method.
This method will take a picayune longer and likely cost more than the PEMT method.
Best suited for:
About if non all translation purposes.
33. Human being Translation + Revision
What is it?
A human translation with an additional review by a second translator.
The review is essentially a safety check – designed to pick upward any translation errors and refine wording if demand exist.
Pros and cons
This produces the highest level of translation quality.
Information technology's as well the about expensive of the four methods, and takes the longest.
Best suited for:
All translation purposes.
At that place's also one other common term used by practitioners and academics alike to draw a blazon (method) of translation:
34. Computer-Assisted Translation (Cat)
What is it?
A human being translator using computer tools to assistance the translation process.
Key features
Virtually all translators use such tools these days.
The well-nigh prevalent tool is Translation Memory (TM) software. This creates a database of previous translations that tin can be accessed for time to come work.
TM software is particularly useful when dealing with repeated and closely-matching text, and for ensuring consistency of terminology. For certain projects information technology can speed upwards the translation process.
The translation methods described by academia
A great deal has been written within academia analysing how human translators get about their arts and crafts.
Seminal has been the piece of work of Newmark, and the post-obit methods of translation attributed to him are widely discussed in the literature.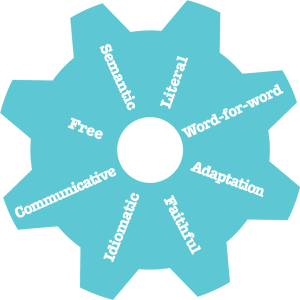
These methods are approaches and strategies for translating the text as a whole, not techniques for handling smaller text units, which we discuss in our terminal translation category.
35. Give-and-take-for-word Translation
This method translates each discussion into the other linguistic communication using its most common pregnant and keeping the discussion order of the original language.
So the translator deliberately ignores context and target language grammar and syntax.
Its chief purpose is to help understand the source linguistic communication structure and give-and-take use.
Oft the translation will exist placed below the original text to aid comparing.
36. Literal Translation
Words are again translated independently using their most common meanings and out of context, but word lodge inverse to the closest acceptable target language grammatical structure to the original.
Its main suggested purpose is to assist someone read the original text.
37. Faithful Translation
Faithful translation focuses on the intention of the author and seeks to convey the precise meaning of the original text.
It uses correct target linguistic communication structures, only structure is less important than meaning.
38. Semantic Translation
Semantic translation is also author-focused and seeks to convey the exact meaning.
Where it differs from faithful translation is that information technology places equal emphasis on aesthetics, ie the 'sounds' of the text – repetition, word play, assonance, etc.
In this method form is as important every bit meaning as information technology seeks to "recreate the precise flavour and tone of the original" (Newmark).
39. Chatty Translation
Seeks to communicate the message and meaning of the text in a natural and easily understood way.
Information technology's described as reader-focused, seeking to produce the same effect on the reader as the original text.
A good comparing of Communicative and Semantic translation tin be found hither.
40. Free Translation
Here conveying the pregnant and upshot of the original are all important.
There are no constraints on grammatical form or word pick to achieve this.
Ofttimes the translation will paraphrase, so may be of markedly different length to the original.
41. Adaptation
Mainly used for poetry and plays, this method involvesre-writing the text where the translation would otherwise lack the same resonance and impact on the audience.
Themes, storylines and characters will generally be retained, simply cultural references, acts and situations adapted to relevant target culture ones.
So this is effectively are-creation of the work for the target civilisation.
42. Idiomatic Translation
Reproduces the meaning or message of the text usingidioms andcolloquial expressions and linguistic communication wherever possible.
The goal is to produce a translation with language that is asnatural equally possible.
Translation Category D: 9 types of translation based on the translation technique used
These translation types are specific strategies, techniques and procedures for dealing with brusque chunks of text – generally words or phrases.
They're often thought of as techniques for solving translation problems.
They differ from the translation methods of the previous category which deal with the text as a whole.

43. Borrowing
What is it?
Using a word or phrase from the original text unchanged in the translation.
Key features
With this procedure we don't translate the word or phrase at all – we merely 'borrow' it from the source language.
Borrowing is a very mutual strategy across languages. Initially, borrowed words seem clearly 'strange', only as they become more familiar, they tin can lose that 'foreignness'.
Translators utilise this technique:
– when it's the best discussion to use – either because information technology has become the standard, or it's the near precise term, or
– for stylist consequence – borrowings can add a prestigious or scholarly season.
Borrowed words or phrases are often italicised in English language.
Examples of borrowings in English
m prix, kindergarten, tango, perestroika, barista, sampan, karaoke, tofu
44. Transliteration
What is information technology?
Reproducing the guess sounds of a name or term from a language with a different writing system.
Key features
In English we use the Roman (Latin) alphabet in mutual with many other languages including almost all European languages.
Other writing systems include Arabic, Cyrillic, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Thai, and the Indian languages.
Transliteration from such systems into the Roman alphabet is too chosen romanisation.
There are accepted systems for how individual letters/sounds should be romanised from well-nigh other languages – there are three mutual systems for Chinese, for example.
English borrowings from languages using non-Roman writing systems also crave transliteration – perestroika, sampan, karaoke, tofu are examples from the above list.
Translators mostly utilize transliteration as a process for translating proper names.
Examples
毛泽东 Mao Tse-tung or Mao Zedong
Владимир Путин Vladimir Putin
서울 Seoul
ភ្នំពេញ Phnom Penh
45. Calque or Loan Translation
What is it?
A literal translation of a foreign word or phrase to create a new term with the same meaning in the target language.
So a calque is a borrowing with translation if you similar. The new term may be changed slightly to reflect target language structures.
Examples
German language 'Kindergarten' has been calqued as детский сад in Russian, literally 'children garden' in both languages.
Chinese 洗腦 'wash' + 'encephalon' is the origin of 'brainwash' in English.
English language skyscraper is calqued as gratte-cielin French andrascacielosin Castilian, literally 'scratches sky' in both languages.
46. Word-for-discussion translation
What is it?
A literal translation that is natural and correct in the target language.
Alternative names are 'literal translation' or 'metaphrase'.
Note: this technique is different to the translation method of the same proper noun, which does not produce correct and natural text and has a different purpose.
Key features
This translation strategy will only work between languages that have very similar grammatical structures.
And even and then, only sometimes.
For example, standard word club in Turkish is Subject field-Object-Verb whereas in English information technology'due south Bailiwick-Verb-Object. So a literal translation between these two will seldom piece of work:
– Yusuf elmayı yedi is literally 'Joseph the apple ate'.
When give-and-take-for-word translations don't produce natural and correct text, translators resort to some of the other techniques described beneath.
Examples
French 'Quelle heure est-il?' works into English language every bit 'What time is information technology?'.
Russian 'Oн хочет что-нибудь поесть' is 'He wants something to swallow'.
47. Transposition
What is it?
Translation with a change of grammatical structure.
This technique gives the translation more than natural wording and/or makes it grammatically correct.
Examples
A change in discussion society:
Our Turkish example Yusuf elmayı yedi (literally 'Joseph the apple ate') –> Joseph ate the apple.
Spanish La Casa Blanca (literally 'The House White') –> The White Business firm
A change in grammatical category:
German Er hört gerne Musik (literally 'he listens gladly [to] music')
= field of study pronoun + verb + adverb + substantive
becomes Spanish Le gusta escuchar música (literally '[to] him [it] pleases to listen [to] music')
= indirect object pronoun + verb + infinitive + noun
and English language He likes listening to music
= field of study pronoun + verb + gerund + noun.
48. Modulation
What is it?
Translation with a change of focus or point of view in the target language.
This technique makes the translation more than idiomatic – how people would ordinarily say it in the linguistic communication.
Examples
English talks of the 'summit floor' of a building, French the dernier étage = final floor. 'Last floor' would be unnatural in English, and then too 'top floor' in French.
German uses the term Lebensgefahr (literally 'danger to life') where in English we'd be more likely to say 'risk of expiry'.
In English language nosotros'd say 'I dropped the fundamental', in Spanish se me cayó la llave, literally 'the fundamental barbarous from me'. The English language perspective is that I did something (dropped the fundamental), whereas in Spanish something happened to me – I'm the recipient of the action.
49. Equivalence or Reformulation
What is it?
Translating the underlying concept or pregnant using a totally different expression.
This technique is widely used when translating idioms and proverbs.
And it's mutual in titles and advertising slogans.
It'due south a common strategy where a straight translation either wouldn't make sense or wouldn't resonate in the same way.
Examples
Here are some equivalents of the English saying "Pigs may fly", significant something will never happen, or "you're being unrealistic" (Source):
– Thai: ชาติหน้าตอนบ่าย ๆ – literally, '1 afternoon in your next reincarnation'
– French: Quand les poules auront des dents – literally, 'When hens have teeth'
– Russian, Когда рак на горе свистнет – literally, 'When a lobster whistles on top of a mountain'
– Dutch, Als de koeien op het ijs dansen – literally, 'When the cows trip the light fantastic toe on the water ice'
– Chinese: 除非太陽從西邊出來!– literally, 'Only if the dominicus rises in the west'
50. Adaptation
What is information technology?
A translation that substitutes a culturally-specific reference with something that's more than relevant or meaningful in the target linguistic communication.
It's also known every bit cultural commutation or cultural equivalence.
Information technology'south a useful technique when a reference wouldn't be understood at all, or the associated nuances or connotations would be lost in the target linguistic communication.
Note: the translation method of the aforementioned proper name is a similar concept but practical to the text every bit a whole.
Examples
Dissimilar cultures celebrate different coming of age birthdays – 21 in many cultures, 20, xv or 16 in others. A translator might consider changing the age to the target culture custom where the coming of age implications were of import in the original text.
Animals have different connotations across languages and cultures. Owls for case are associated with wisdom in English, but are a bad omen to Vietnamese. A translator might want to remove or amend an fauna reference where this would create a unlike image in the target language.
51. Bounty
What is it?
A pregnant or dash that can't be directly translated is expressed in some other way in the text.
Example
Many languages have ways of expressing social status (honorifics) encoded into their grammatical structures.
And then you can convey different levels of respect, politeness, humility, etc simply past choosing different forms of words or grammatical elements.
But these nuances will be lost when translating into languages that don't have these structures.
So a translator might use this strategy to express (compensate for) them in some other style – perhaps by using a unlike register (vocabulary that's more formal or informal) or by calculation something non in the original.
Then there you have it – your comprehensive list of 51 common translation types, methods, techniques and procedures.
Grab a pdf of the list for future reference!
Permit us quote for your side by side translation project!
We're your platonic partner if you need loftier-quality translations
past the very best homo translators .
We'll deliver yous high-quality work – guaranteed
Simply:
– use our translation quote form, or
– e-mail us the details.
We'll be back to you asap.
Are you on our mailing list?
Yous'll become proven, highly practical and quick-read tips for achieving better translation results, direct to your inbox.
Nifty value for just xx seconds of your time, once a fortnight. Sign up now, or read more here.
And brand sure yous haven't missed any of our current articles, guides and videos!
They're listed nether Key articles for clients on our main blog folio.
Here are iii very pop ones to start with:
Back to top | Pactranz web log | Pactranz home page
DOWNLOAD HERE
Posted by: espinosaciver1977.blogspot.com